Unlock Your Mind: The Impact of Sleep on Mental Health

The Impact of Sleep on Mental Health: Tips for Improving Your Sleep Hygiene explores how crucial sleep is for psychological well-being and offers actionable advice for a healthier sleep routine.
In today’s fast-paced world, prioritizing the impact of sleep on mental health: tips for improving your sleep hygiene often takes a backseat. However, the link between sleep and mental well-being is undeniable, influencing everything from mood regulation to cognitive function.
Understanding the Sleep-Mental Health Connection
Sleep is not merely a period of rest; it’s a vital process that allows our brains to consolidate memories, process emotions, and repair cellular damage. When we consistently fall short on sleep, these crucial functions are compromised, leading to a cascade of negative effects on our mental health.
The connection between sleep deprivation and mental health issues is a complex and bidirectional relationship. Mental health conditions can often disrupt sleep, creating a vicious cycle. Poor sleep can exacerbate existing mental health conditions, while conversely, improving sleep hygiene can have a positive impact on mental well-being.
The Science Behind Sleep and the Brain
During sleep, our brains go through various stages, each playing a different role in cognitive function and emotional regulation. Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is particularly important for physical restoration and memory consolidation. REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is characterized by heightened brain activity and is crucial for emotional processing and creativity.
Hormones also play a significant role in the sleep-wake cycle. Melatonin, often referred to as the “sleep hormone,” is produced by the pineal gland and helps regulate our circadian rhythm, the body’s internal clock. Cortisol, the stress hormone, also follows a daily rhythm, with levels typically higher in the morning and lower in the evening. Disruptions to these hormonal patterns can contribute to sleep disturbances and mental health issues.
- Neurotransmitters and Sleep: Sleep affects neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood.
- Brain Wave Activity: Different sleep stages correlate with distinct brain wave patterns, impacting cognitive processing.
- The Role of the Circadian Rhythm: Understanding our body’s internal clock is crucial for optimal sleep and mental health.
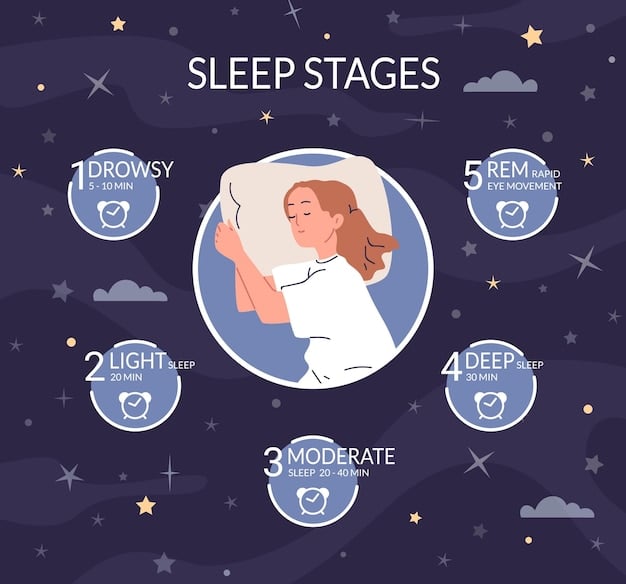
In conclusion, understanding the intricate interplay between sleep and brain function is crucial for appreciating the impact of sleep on mental health. By recognizing the scientific underpinnings of sleep, we can take informed steps to prioritize sleep and promote overall well-being.
The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Mood
One of the most immediate and noticeable effects of sleep deprivation is its impact on mood. Even a single night of poor sleep can leave you feeling irritable, anxious, and emotionally volatile. Chronic sleep deprivation can significantly increase the risk of developing mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
Research has consistently shown a strong correlation between sleep disturbances and mood dysregulation. Individuals who consistently sleep less than seven hours per night are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, including feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
Sleep Deprivation and Anxiety
Sleep deprivation can also fuel anxiety, making it difficult to manage stress and cope with everyday challenges. When we are sleep-deprived, our brains are more reactive to negative stimuli, leading to an exaggerated sense of worry and fear.
Studies have indicated that individuals with anxiety disorders often experience significant sleep disturbances, such as insomnia and restless legs syndrome. Addressing sleep issues can be a crucial component of anxiety management, helping to reduce worry and improve overall coping skills.
- Increased Irritability: Lack of sleep lowers the threshold for frustration.
- Emotional Volatility: Sleep deprivation can lead to mood swings and difficulty regulating emotions.
- Risk of Mood Disorders: Chronic sleep loss increases the likelihood of developing depression and anxiety.
Ultimately, recognizing the profound impact of sleep deprivation on mood is essential for proactive mental health management. By prioritizing sleep, we can mitigate mood swings, manage anxiety, and foster a more positive emotional state.
Cognitive Function and Sleep: How Sleep Affects Your Brain
Beyond its impact on mood, sleep also plays a crucial role in cognitive function, affecting everything from memory and attention to decision-making and problem-solving. When we are sleep-deprived, our cognitive abilities are significantly impaired, making it difficult to perform at our best both personally and professionally.
The brain relies on sleep to consolidate memories, transferring information from short-term to long-term storage. During sleep, the brain also clears out toxins and waste products that accumulate throughout the day, promoting optimal cognitive performance. Lack of sleep disrupts these essential processes, leading to cognitive deficits.
Impact on Memory and Learning
Sleep is essential for both the encoding and retrieval of memories. During sleep, the brain replays and strengthens newly formed connections, making it easier to recall information later on. Sleep deprivation impairs this process, leading to difficulties with learning and memory.
Studies have shown that students who get adequate sleep perform significantly better on exams and retain information more effectively. Prioritizing sleep is therefore crucial for academic success and lifelong learning.
- Reduced Attention Span: Sleepiness impairs focus and concentration.
- Impaired Decision-Making: Sleep deprivation affects the ability to make sound judgments.
- Difficulty with Problem-Solving: Lack of sleep reduces cognitive flexibility and creativity.

In summary, sleep is essential for optimizing cognitive function, from memory and attention to decision-making and problem-solving. By prioritizing sleep, we can enhance our cognitive abilities, improve performance, and unlock our full potential.
Practical Tips for Improving Your Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene includes behaviors, environmental factors, and daily routines that can influence the quality and quantity of your sleep. Implementing these strategies can lead to significantly improved sleep quality and overall mental wellness.
Improving your sleep hygiene is a process, and it may take time to establish new habits. Be patient with yourself, and celebrate small victories along the way. Consistency is key, so stick with your new routine as much as possible, even on weekends.
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and makes it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed. Consistency is key to training your body to anticipate sleep at a certain time each day.
- Set a Morning Alarm: Wake up at the same time, regardless of how well you slept.
- Avoid Oversleeping: Resist the urge to sleep in on weekends; stick to your regular schedule.
- Gradual Adjustments: If you need to adjust your sleep schedule, do so gradually in 15-30 minute increments.
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Develop a calming pre-sleep routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, listening to soothing music, or practicing relaxation techniques.
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Use blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to minimize distractions. Keep the temperature comfortable, ideally between 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit.
Ultimately, improving sleep hygiene involves conscious and consistent efforts to create a sleep-friendly environment and adopt healthy habits. By prioritizing sleep hygiene, individuals can improve their sleep quality, enhance mental well-being, and lead more fulfilling lives.
Diet and Exercise Considerations for Better Sleep
The food we eat and the activities we engage in throughout the day can significantly influence our sleep quality. Making thoughtful choices about diet and exercise can contribute to a more restful night’s sleep and enhanced overall well-being.
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to diet and exercise for sleep, certain guidelines can be generally beneficial. Experiment with different strategies and find what works best for you and your individual needs.
Dietary Guidelines for Sleep
Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with your ability to fall asleep, while alcohol can disrupt your sleep cycle and lead to fragmented sleep.
Limit sugary and processed foods, especially in the evening. These foods can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes that disrupt sleep. Opt for a light, healthy snack if you’re feeling hungry before bed, such as a handful of nuts or a small bowl of yogurt.
- Hydration: Avoid drinking excessive liquids before bed to minimize nighttime awakenings.
- Bedtime Snacks: A small snack containing tryptophan, like turkey or bananas, may promote relaxation.
- Meal Timing: Avoid heavy meals close to bedtime to prevent digestive discomfort.
Exercise and Sleep Quality
Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but it’s important to time your workouts appropriately. Avoid strenuous exercise close to bedtime, as it can increase your heart rate and make it difficult to fall asleep.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Exercise can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and reduce stress, leading to better sleep.
In conclusion, thoughtful consideration of diet and exercise is essential for optimizing sleep quality and supporting overall health. By implementing these strategies, individuals can promote restful sleep, enhance physical health, and improve their general well-being.
Seeking Professional Help for Sleep Disorders
While many sleep problems can be addressed through lifestyle modifications and sleep hygiene practices, some individuals may require professional help. Sleep disorders are common and treatable, and seeking assistance from a healthcare provider can be a crucial step towards improved sleep and overall well-being.
If you experience persistent sleep problems that significantly impact your daily life, it’s essential to consult with a doctor or sleep specialist. They can help diagnose any underlying sleep disorders and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Common Sleep Disorders
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and medical conditions.
Sleep apnea is a condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This can lead to fragmented sleep, daytime sleepiness, and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
- Narcolepsy: A neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks.
- Parasomnias: These include sleepwalking, sleep terrors, and REM sleep behavior disorder.
To sum up, seeking professional help from a medical professional is a crucial step when dealing with persistent sleep disorders. By seeking appropriate medical treatment, individuals can improve sleep latency, enhance mental wellness, and lead healthier, more productive lives.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 😴 Sleep’s Impact | Vital for brain function and emotional regulation. |
| 🧠 Cognitive Benefits | Enhances memory, attention, and decision-making. |
| 🛌 Sleep Hygiene | Establish routines and optimize sleep environment. |
| 🩺 Professional Help | Seek guidance for persistent sleep disorders. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Sleep deprivation leads to increased irritability and emotional volatility, making mood swings more common. Adequate sleep helps regulate emotions and maintain a stable mood.
Yes, poor sleep impairs memory consolidation and retrieval. During sleep, your brain strengthens memories, making them easier to recall when you’re awake and alert.
A relaxing routine might include a warm bath, reading, or gentle yoga. Avoid screens, caffeine, and heavy meals before bed. Consistency helps signal your body it’s time to sleep.
Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. Use blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine, and adjust the temperature to between 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit for optimal sleep.
Seek professional help if sleep problems persist, impact daily life, or if you suspect a sleep disorder. A doctor can diagnose and treat underlying issues for improved sleep health.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, the impact of sleep on mental health: tips for improving your sleep hygiene are significant and far-reaching. From mood regulation to cognitive function, quality sleep is an essential pillar of overall well-being. By implementing consistent sleep hygiene practices, making mindful dietary choices, and seeking professional help when needed, you can unlock the power of sleep and cultivate a healthier, happier, and more balanced life.





